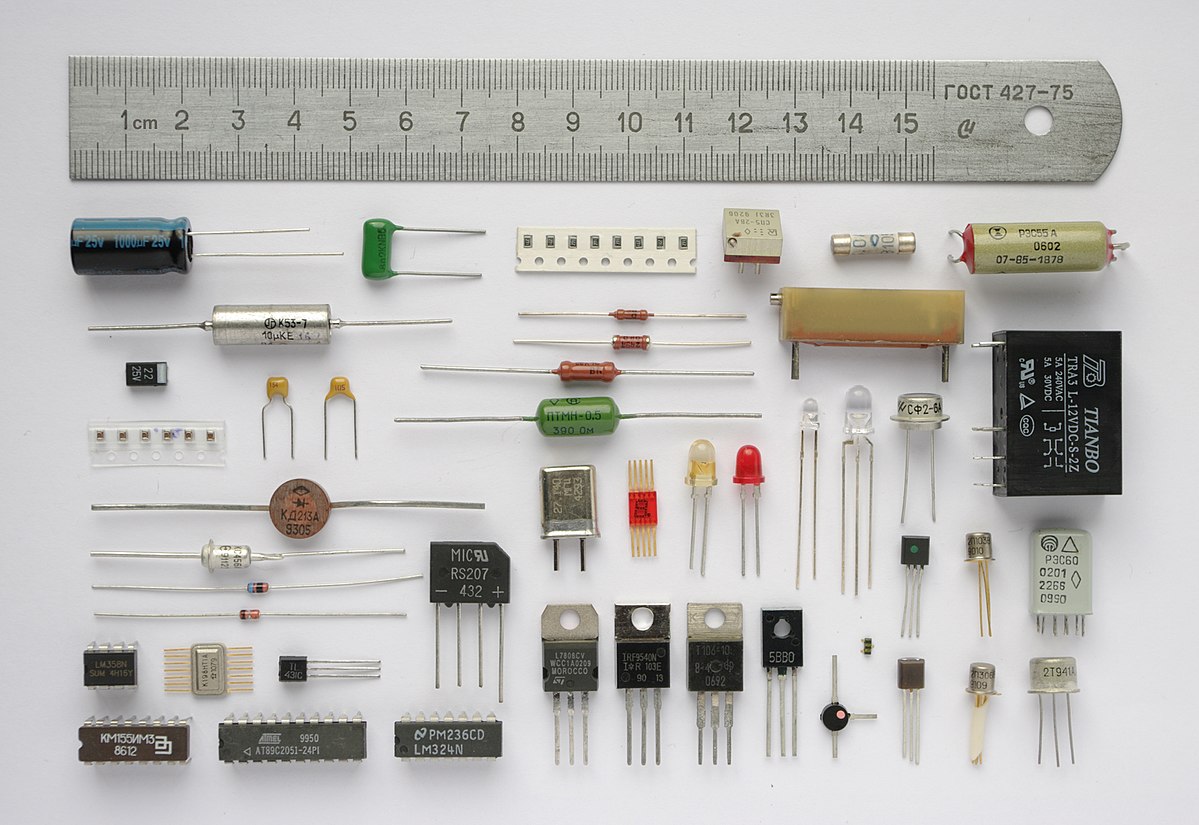
Electronic components can be summarized in a shortlist. Here are more details about these essential components of modern electronics.
What are the electronic components?
The following components are the most common components found in electronic devices.
- Microcontrollers
- Transformer
- Batteries
- Fuses
- Relays
- Switches
- Motor
- Circuit Breaker
What are the uses of electronic components?
Microcomputers are small computers that control various devices, such as power tools, remote controls, medical equipment, and office machines. A battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The two different cells of a battery are the anode (+) and the cathode (-).
Fuses help prevent components from being overloaded by excessive current. The fuse consists of a connector, bracket, contacts, and a metal fuse material (e.g., zinc or copper). A remote switch can control the circuit breaker as a protective device. It is designed to protect the circuit from overloads or short circuits.
Relays are electromechanical switches that turn off or shut off the power. A relay consists of a solenoid, an armature, a series of electrical contacts, and a spring.
Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include the rotor, stator, bearings, conduit box, housing, and eyebolt. Electric motors can power various devices, from watches to home entertainment devices to vehicles.
What are the active and passive components in electronics?
Active components include transistors, while passive components include transformers, inductors, resistors, and capacitors. Transformers are typically used in step-up or step-down power supplies. A resistor limits the current. It is used in thermistors and potentiometers. Similar to low-capacity batteries, capacitors allow for delays in the circuit. Inductors are used to control frequency.
You will use many basic electronic components when building electronic circuits, including resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, inductors, and integrated circuits. The following is a brief overview of the components and their functions.
Integrated Circuits: An integrated circuit is a special device with all the components needed for an electronic circuit. The component has diodes, transistors, and other devices, all etched onto a small piece of silicon. These components are used in many electronic devices, including watches and computers.
Resistors: A resistor is one of the components you will encounter in an integrated circuit. As the name implies, the device resists electrical currents. Resistors are graded according to their power rating (the amount of power they can handle without exploding) and their resistance value (their ability to resist current). Measurements are made in units called ohms. The electronic symbol for the unit is O.
Capacitors: These components can temporarily store electrical charges. There are different types of these components, the most common being electrolytic and ceramic disks. The capacity of the component is usually measured in microfarads (µF).
Diodes: Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. Each diode has two terminals, called anode and cathode. Current can flow when the anode is charged with a positive voltage, and the cathode is charged with a negative voltage. Reversing these voltages will prevent the current from flowing.
Transistors: These components are easily identified by their three terminals. For the component to work, a voltage must be applied to the base terminal. The base terminal can then control the current in the other two terminals (emitter and collector).
Inductors: These are passive components that store energy in the form of a magnetic field. Inductors consist only of coils wound on a magnetic core of some kind. The core can be a magnet or air. When current passes through an inductor, it creates a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field will be stronger if a magnet is used as the core.
Microcontroller: Microcontrollers are small computers that control various devices, such as power tools, remote controls, medical devices, and office machines.
Transformer: Consisting of two coils, transformers are typically used in step-up or step-down power supplies.
Battery: A battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy. The two different cells of a battery are the anode (+) and the cathode (-).
Fuses: Fuses help prevent components from being overloaded due to excessive current. A fuse consists of a connector, bracket, contacts, and a metal fuse material (such as zinc or copper).
Relays: These electromechanical switches turn the power on or off. Relays consist of a solenoid, an armature, a series of electrical contacts, and a spring.
Switches: Switches interrupt the current. The four types of switches are single pole single throw (SPST), single Pole double throw (SPDT), Double pole single throw (DPST), and double pole double throw (DPDT).
Motor: A motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Key components include rotors, stators, bearings, conduit boxes, housings, and eyebolts.Circuit Breaker: As a protective device, a remote switch can control the circuit breaker. It is designed to protect circuits from overloads or short circuits.





More Stories
12 Benefits of Using Yext for Your SEO Strategy
How a Revops Agency Can Eliminate Chaos and Create Revenue Clarity
Why Exhibit Fabrication Is the Key to Memorable Brand Experiences